

This result may be due to a failing hard drive, as one of the crucial functions that drive error checking performs is to identify and block bad sectors on the drive. Some end users who follow the suggested steps may find that their hard drive space significantly reduced after running the command. Once the process is complete, a summary of the results, including any errors found and repairs made, can be found in the Windows Event Viewer under the Application folder within Windows Logs. NoteĬhecking for drive errors can take a long time, especially when performed on larger drives. During the repair process, the progress will be displayed on the screen. The repair will start automatically before the next Windows startup. Exit all programs and then restart your system. Click Scan drive action to proceed.ġ.7 Windows will proceed to scan the drive for errors and will immediately perform any repairs that can be done without requiring a restart.ġ.8 Once the scan is complete, Windows will inform you if it detected any errors, and if so, whether it was able to successfully repair errors without requiring a restart.ġ.9 If Windows detected one or more errors that require a restart, you'll be prompted to restart. On the center panel, under Devices and drives, storage devices are displayed.ġ.3 Right-click the drive you'd like to check (such as C:) and select Properties.ġ.5 Under Error Checking, click the Check button.ġ.6 If there are no unresolved errors that were previously detected, Windows will confirm if you want to scan the drive for errors anyway. (Right-click Windows Start Menu, located in lower left corner of screen, click File Explorer.)ġ.2 Click This PC, located on the left side panel. You must have administrative privileges to run these processes.įollow the steps below to scan all internal storage drives (OS, secondary, and so on) for potential file integrity/structure errors.ġ.1 Open File Explorer.This guidance may be modified periodically, so check the source on to ensure you have the latest version.During this process, reboots may occur.The following tools can be used with Intel® Optane™ memory enabled and/or disabled.It's recommended to remove all externally connected storage devices (USB, SD Card, and so on).Ensure your system is operational (that is, if you can log in and interact with Windows*).

Important information prior to starting these processes: The time it takes to complete this process varies depending on system configuration, but may take up to one hour for all steps.
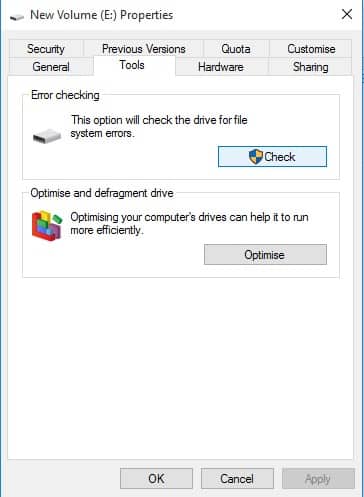
If you're comfortable with command-line interface or have similar technical knowledge, you can follow the manual steps provided below to check the integrity of the information on your systems.Įnsure your data is backed up, then follow the detailed instructions provided.
End users who are interested in checking the integrity of information on systems disk drives should refer to the guidance below.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
